Understanding Osteoarthritis in Knee and Hip Joints: Key Insights and Risk Factors
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that primarily affects the cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced joint function. It is one of the most common joint disorders and significantly impacts the quality of life. The knee and hip joints are particularly vulnerable to OA due to their anatomical and functional characteristics.
Understanding why osteoarthritis is common in these joints is crucial for early intervention, effective treatment, and improved outcomes. Prompt diagnosis and management can help alleviate symptoms and slow disease progression.
Types of Osteoarthritis:
- Primary Osteoarthritis: Occurs without an underlying cause, often related to aging and wear-and-tear.
- Secondary Osteoarthritis: Develops due to a specific cause, such as joint injury, obesity, or genetic conditions.
Why Is Osteoarthritis Common in the Knee and Hip Joints?
Anatomy and Function of the Knee and Hip Joints
The knee and hip joints are weight-bearing structures that support the body’s movement and stability. These joints are subjected to significant stress and repetitive motion, making them highly susceptible to degeneration.
- Weight-bearing nature: Both joints bear the body’s weight during activities such as walking, running, and standing.
- High mobility: The knee and hip joints are highly mobile, contributing to their vulnerability to repetitive strain and injuries.
Common Osteoarthritis Causes for Knee and Hip Joints
Understanding the causes of osteoarthritis in these joints helps in prevention and management:
- Aging and wear-and-tear: The natural aging process leads to the gradual breakdown of joint cartilage.
- Obesity and its impact on joint load: Excess weight increases the load on the knee and hip joints, accelerating cartilage wear.
- Previous injuries or trauma: Joint injuries can lead to early onset osteoarthritis.
- Genetic predisposition: Family history of OA can increase the risk of developing it.
- Structural abnormalities: Conditions such as hip dysplasia or bow-legged alignment contribute to OA.
Types of Osteoarthritis:
- Primary Osteoarthritis: Occurs without an underlying cause, often related to aging and wear-and-tear.
- Secondary Osteoarthritis: Develops due to a specific cause, such as joint injury, obesity, or genetic conditions.
Why Is Osteoarthritis Common in the Knee and Hip Joints?
Anatomy and Function of the Knee and Hip Joints
The knee and hip joints are weight-bearing structures that support the body’s movement and stability. These joints are subjected to significant stress and repetitive motion, making them highly susceptible to degeneration.
- Weight-bearing nature: Both joints bear the body’s weight during activities such as walking, running, and standing.
- High mobility: The knee and hip joints are highly mobile, contributing to their vulnerability to repetitive strain and injuries.
Common Osteoarthritis Causes for Knee and Hip Joints
Understanding the causes of osteoarthritis in these joints helps in prevention and management:
- Aging and wear-and-tear: The natural aging process leads to the gradual breakdown of joint cartilage.
- Obesity and its impact on joint load: Excess weight increases the load on the knee and hip joints, accelerating cartilage wear.
- Previous injuries or trauma: Joint injuries can lead to early onset osteoarthritis.
- Genetic predisposition: Family history of OA can increase the risk of developing it.
- Structural abnormalities: Conditions such as hip dysplasia or bow-legged alignment contribute to OA.
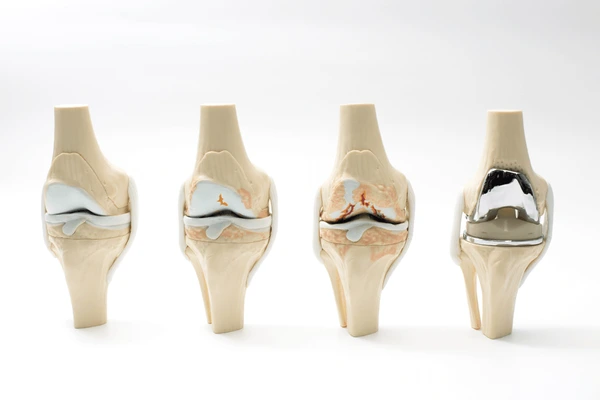
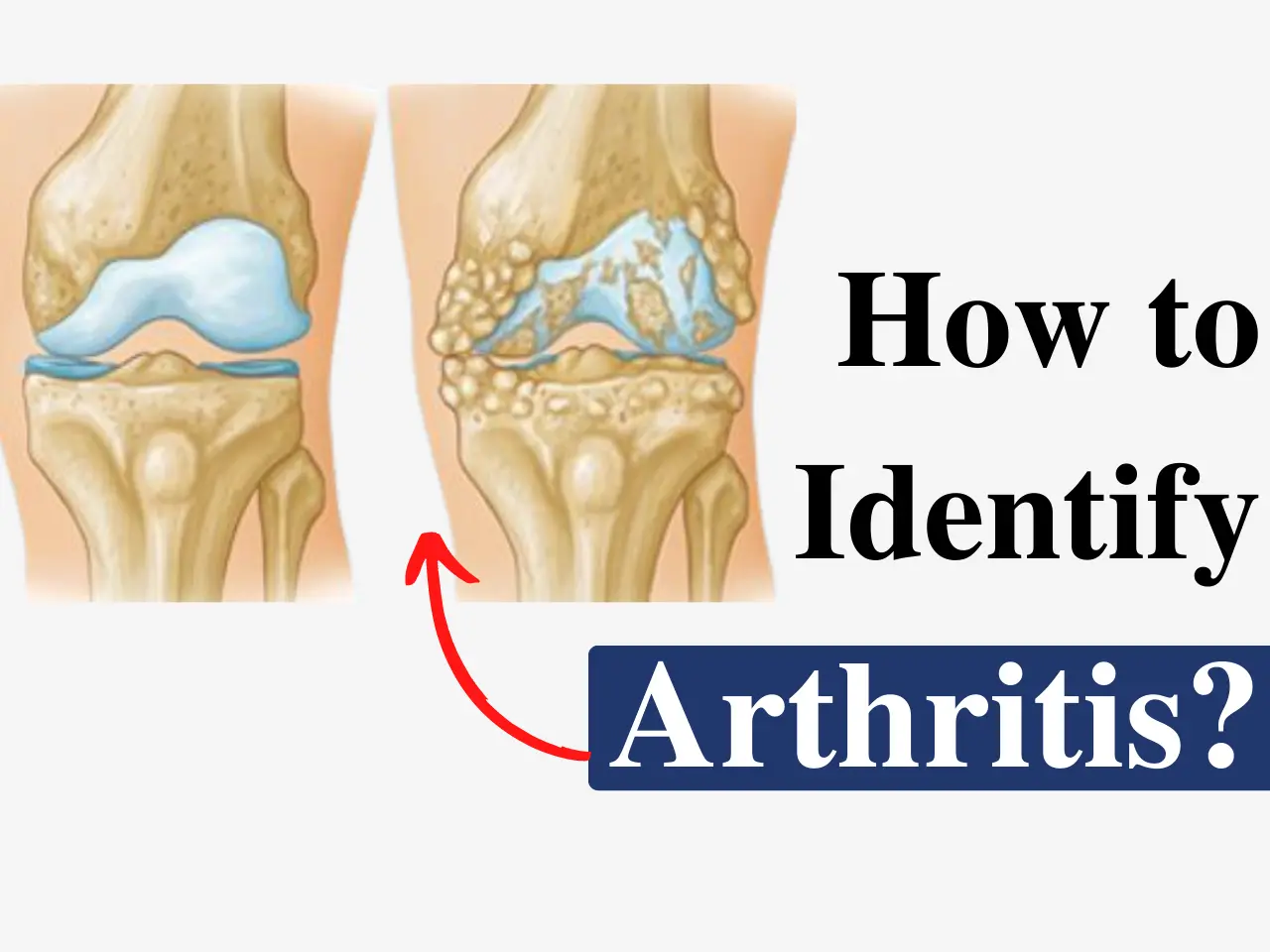
Stages of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis progresses through different stages, which are crucial for determining treatment options:
- Minor (Stage 1): Minimal damage, few or no symptoms.
- Mild (Stage 2): Noticeable wear-and-tear, mild pain, and stiffness.
- Moderate (Stage 3): Cartilage erosion, increased discomfort, and reduced range of motion.
- Severe (Stage 4): Significant cartilage loss, constant pain, and limited joint function.
Osteoarthritis Diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis is essential for managing osteoarthritis effectively:
Clinical evaluation: Performed by an orthopaedic specialist to assess symptoms and joint function.
Imaging tests:
- X-rays: To view bone changes and joint space narrowing.
- MRI scans: Provide detailed images of cartilage and soft tissues.
Laboratory tests: Used to rule out other conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
How to Prevent Osteoarthritis?
Lifestyle Changes
Prevention plays a vital role in reducing the risk of osteoarthritis:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Helps reduce joint stress and prevents excessive wear.
- Regular, low-impact exercises: Activities such as swimming and cycling strengthen muscles without overloading joints.
- Balanced diet: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports joint health.
Early Intervention
Addressing issues promptly can help prevent OA progression:
- Treating joint injuries early: Reduces the risk of future OA.
- Using assistive devices: Can help reduce joint strain.
- Avoiding repetitive stress: Proper techniques during activities can prevent joint damage.
Osteoarthritis Knee Treatment and Hip Management Options
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Physical therapy: Strengthens surrounding muscles and improves joint function.
- Pain relief medications: NSAIDs can help manage pain and inflammation.
Injections:
- Corticosteroids: Provide temporary pain relief.
- Hyaluronic acid: Lubricates the joint, improving mobility.
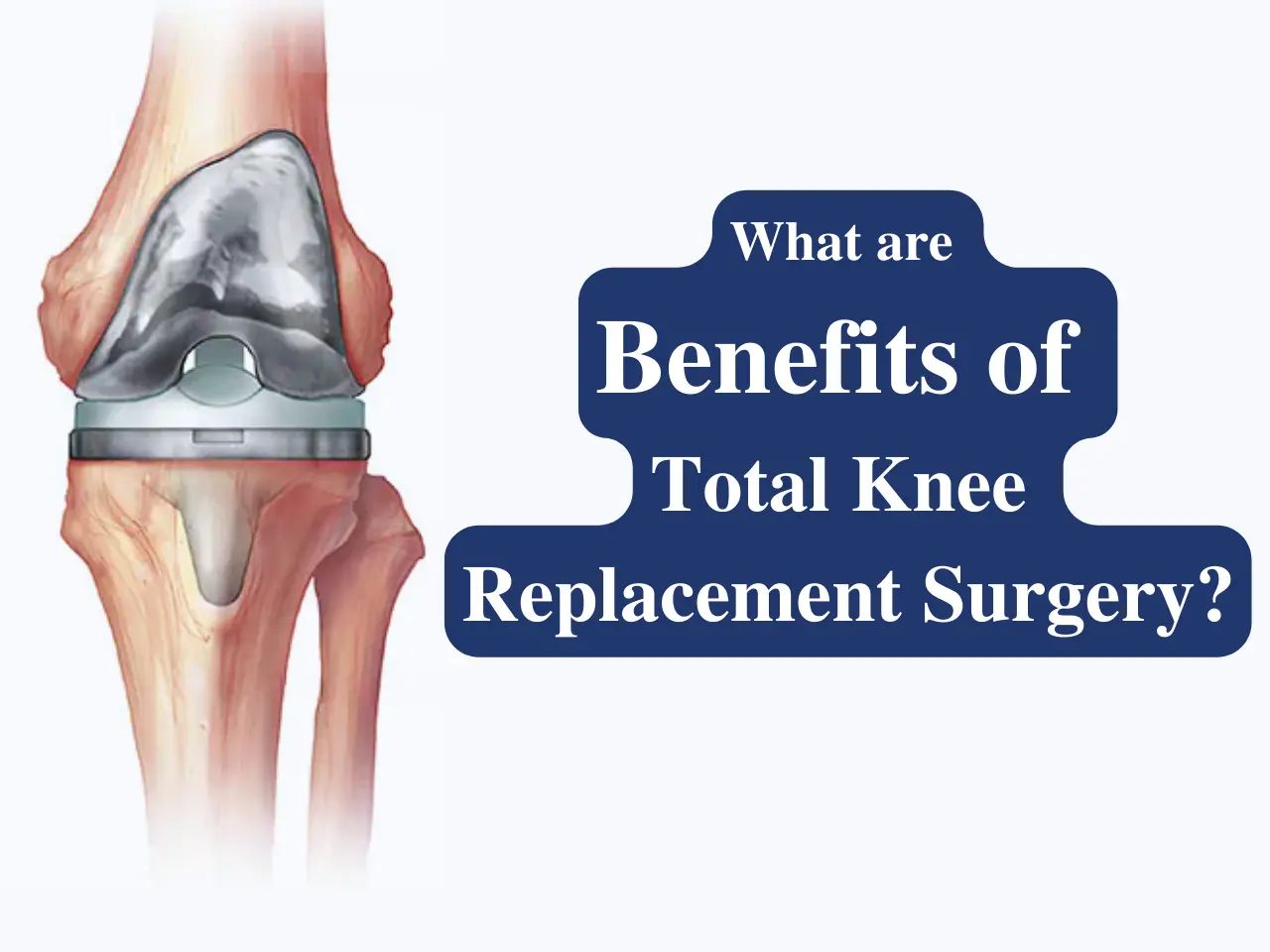
Surgical Options
Partial or total knee replacement: Suitable for advanced OA, restoring function and reducing pain.
Hip replacement surgery:
- Role of a hip replacement surgeon in Cheshire: Specialized surgeons ensure successful outcomes through advanced techniques.
- Advanced surgical techniques: Minimally invasive procedures have improved recovery times and outcomes.
Living with Osteoarthritis of the Hip & Knee
Managing life with OA involves more than just medical treatment:
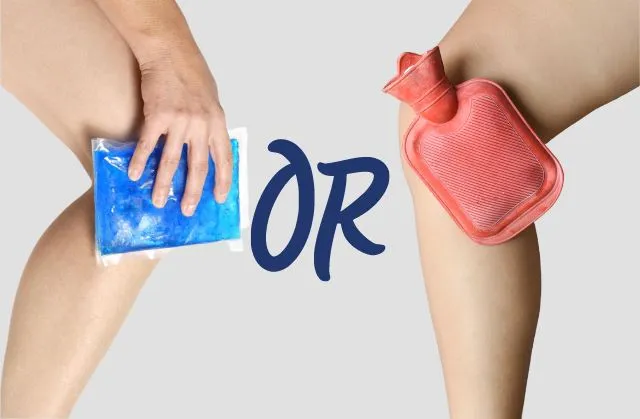
- Managing chronic pain: Techniques like hot/cold therapy and pain management programs.
- Supportive care and assistive devices: Can help maintain independence.
- Psychological and emotional coping strategies: Counseling and support groups can help manage the emotional impact.
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis is prevalent in the knee and hip joints due to their anatomy, high mobility, and weight-bearing nature. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and stages is key for effective prevention and treatment.
Proactive management, including consultation with experienced specialists like Prof. Nikhil Pradhan, can make a significant difference in managing osteoarthritis and maintaining quality of life.