Introduction
A tendon is a cord of strong, flexible tissue, similar to a rope. Tendons connect your muscles to your bones.
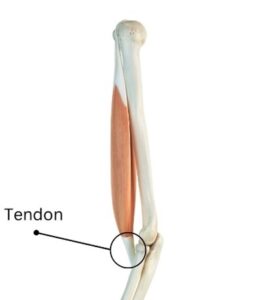
Tendonitis, also spelled tendinitis, is a common condition that involves inflammation or irritation of a tendon, the thick fibrous cords that attach muscle to bone. This condition can cause significant pain and discomfort, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life. Understanding tendonitis is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
This blog will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatments of tendonitis, providing comprehensive insights for those affected by this condition.
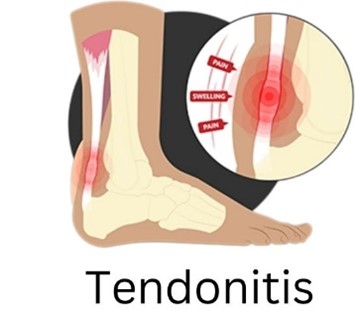
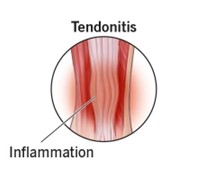
What is Tendonitis?
Tendonitis refers to the inflammation of a tendon, often resulting from repetitive motion or overuse. It is a condition that commonly affects athletes, manual labourers, and individuals who perform repetitive tasks.
Tendonitis should not be confused with tendinosis, which involves the degeneration of the tendon’s collagen in response to chronic overuse without inflammation.
Tendonitis Symptoms:
- Pain: The hallmark symptom of tendonitis is pain at the site of the affected tendon, often described as a dull ache. This pain typically worsens with movement and may improve with rest.
- Tenderness: The area around the inflamed tendon will likely be tender to the touch, causing discomfort even with minimal pressure.
- Stiffness and Difficulty Moving: Tendonitis can limit the range of motion in the affected joint, making it difficult to perform everyday activities.
- Swelling: In some cases, the affected area may experience mild swelling, sometimes accompanied by redness or warmth.
- Creaking or Popping: You might hear or feel a crackling or popping sensation when moving the joint, indicating friction within the inflamed tendon sheath.
Specific Areas Affected
Tendonitis can affect various parts of the body. The most commonly affected areas include:
- Achilles Tendonitis: Pain and stiffness in the heel and lower calf.
- Knee Tendonitis: Pain around the kneecap or the tendon connecting the quadriceps to the shinbone.
- Shoulder Tendonitis: Pain and reduced range of motion in the shoulder.
- Elbow Tendonitis: Pain on the outside or inside of the elbow, often referred to as tennis or golfer’s elbow.
Achilles Tendonitis Knee Tendonitis
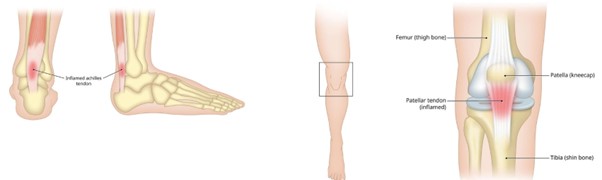
Shoulder Tendonitis Elbow Tendonitis

Tendonitis Causes:
Tendonitis can arise from various factors, but the most common culprit is overuse. Repetitive motions that strain a particular tendon can lead to micro-tears and inflammation.
This is often seen in athletes and individuals with physically demanding jobs.
Here are some other potential causes of tendonitis:
- Improper Technique: Incorrect form during exercise or activities can put undue stress on tendons, increasing the risk of inflammation.
- Sudden Increase in Activity: Rapidly ramping up activity levels without proper conditioning can overwhelm tendons, leading to injury.
- Age-Related Degeneration: As we age, tendons naturally lose elasticity and become more susceptible to tears and inflammation.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and gout can contribute to tendon inflammation.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing tendonitis:
- Occupations with Repetitive Motions: Jobs that involve repetitive tasks can lead to tendon overuse.
- Sports Activities: Athletes in sports requiring repetitive motions, such as tennis or basketball, are at higher risk.
- Age and Lifestyle: Aging and sedentary lifestyles can weaken tendons, making them more prone to inflammation.
Diagnosing Tendonitis
Initial Assessment
The diagnosis of tendonitis typically begins with a thorough initial assessment:
- Patient History: Review of symptoms, medical history, and activities.
- Physical Examination: Examination of the affected area for signs of tenderness, swelling, and reduced range of motion.
Diagnostic Tests
To confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions, several tests may be conducted:
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, and ultrasound can visualize tendon inflammation and damage.
- Blood Tests: Occasionally used to rule out infections or other inflammatory conditions.
Tendonitis Treatment
Treatment for Specific Tendonitis Cases:
While the general principles of treatment apply to most cases, some specific types of tendonitis might require tailored approaches:
- Achilles Tendinitis Treatment: This condition affects the tendon in the heel and often responds well to physical therapy with a focus on eccentric strengthening exercises. In severe cases, a walking boot or orthotics might be recommended.
- Knee Tendonitis Treatment: Depending on the location of the inflammation (patellar tendonitis or pes anserine bursitis), treatment may involve strengthening exercises for the quadriceps and hamstrings, along with patellar taping or bracing for support.
- Shoulder Treatment: It typically responds to a combination of treatments including physical therapy focused on strengthening and flexibility exercises tailored to the shoulder muscles. Rest, ice application, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and swelling. Corticosteroid injections may be considered for more severe cases to reduce inflammation.
- Elbow Treatment: Tennis elbow or golfer’s elbow, often benefits from rest, ice packs, and NSAIDs to manage symptoms. Physical therapy involving specific exercises to strengthen the forearm muscles and improve flexibility is crucial. In some instances, wearing a brace or strap around the affected area can provide additional support during activities that may aggravate the tendonitis
Prevention of Tendonitis
Lifestyle Modifications
Preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing tendonitis:
- Regular Exercise and Proper Warm-Up: Maintaining overall fitness and warming up before activities.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Ensuring workspaces and equipment are ergonomically designed.
Mr.essional Guidance
Seeking professional advice can aid in prevention:
- Consultation with an Orthopaedic Surgeon in Cheshire: Consulting with professionals, such as Mr. Nikhil Pradhan, an orthopaedic surgeon in Cheshire, ensures access to expert care and guidance.
- Role of Ongoing Physical Therapy and Follow-Up: Regular check-ups and therapy to maintain tendon health.
When to See a doctor
Recognizing when to seek medical attention is crucial:
- Indicators for Seeking Medical Attention: Persistent pain, swelling, and reduced function.
- How an Orthopaedic Surgeon in Cheshire Can Help: Nikhil Pradhan provides expert diagnosis, treatment plans, and surgical options if necessary.
Conclusion
Understanding tendonitis is essential for effective management and prevention. By recognizing the symptoms, identifying the causes, and following appropriate treatment plans, individuals can alleviate pain and prevent recurrence.