What is Patellar Tendinopathy?
Patellar tendinopathy, often referred to as “jumper’s knee,” is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation in the patellar tendon. This tendon connects the kneecap (patella) to the shinbone (tibia) and plays a crucial role in facilitating knee movement.
Overuse or repeated stress on this tendon can lead to microscopic tears, resulting in pain and dysfunction.
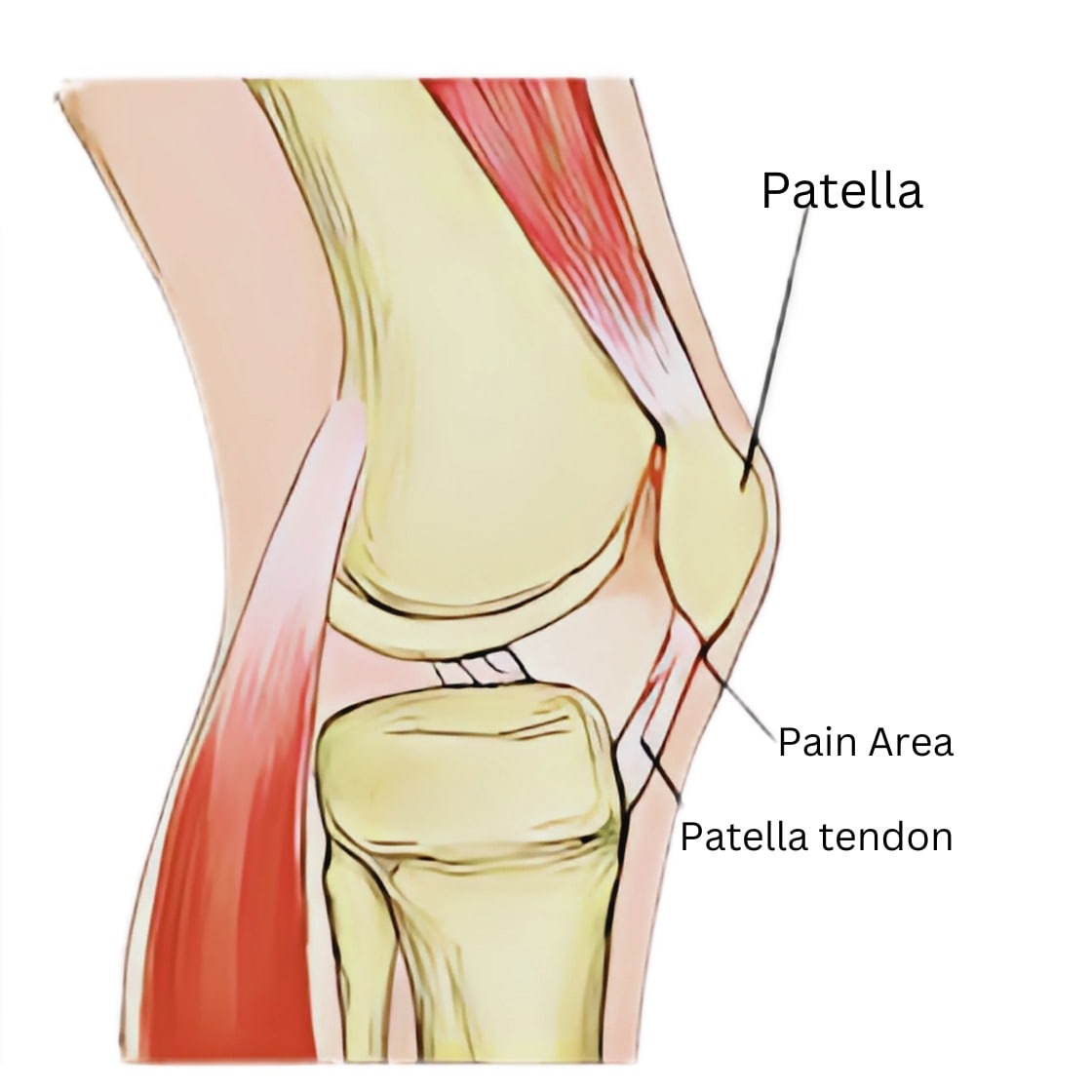
Introduction to Patellar Tendinopathy
Patellar tendinopathy primarily affects individuals involved in sports that require frequent jumping, running, or squatting.
Understanding what patellar tendinitis is essential for effective management and treatment. Unlike general knee pain, this condition specifically involves the patellar tendon, making it a unique and often challenging injury to address.
Early diagnosis and intervention are vital to prevent long-term damage.
Symptoms of Patellar Tendinitis
Recognizing the symptoms of patellar tendinitis can help in seeking timely medical care. Common symptoms include:
- Pain localized at the front of the knee, near the patellar tendon.
- Swelling and tenderness around the kneecap.
- Stiffness, especially after intense physical activity.
- Difficulty performing activities such as jumping, running, or climbing stairs.
If these symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a specialist is crucial to avoid complications.
patellar tendinitis causes
patellar tendinitis often stems from repetitive stress on the knee joint. Common contributors include:
- High-impact sports such as basketball, volleyball, or running.
- Sudden increases in physical activity levels without proper conditioning.
- Biomechanical factors, such as:
- Poor leg alignment.
- Weak or imbalanced muscles around the knee.
These factors can lead to excessive strain on the patellar tendon, increasing the risk of injury.
Risk Factors for Patellar Tendinitis
Several patellar tendinitis risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition:
- Age: Young athletes are more prone due to high activity levels.
- Intense physical activity: Sports that involve repetitive jumping or running.
- Excess body weight: Additional strain on the knees.
- Biomechanical issues: Flat feet, improper footwear, or weak quadriceps muscles.
Identifying and addressing these risk factors can help reduce the chances of developing patellar tendinitis.
Diagnosis of Patellar Tendinopathy
A thorough diagnosis involves:
- Clinical examination by an experienced orthopaedic specialist.
- Imaging tests such as:
- X-rays to exclude other potential causes of knee pain.
- MRI to determine the extent of tendon damage and inflammation.
Accurate diagnosis ensures the right treatment plan is implemented.
Treatment Options for Patellar Tendinitis
Conservative Treatments
For most cases, non-surgical treatments are effective. These include:
- Resting the knee and avoiding aggravating activities.
- Applying ice packs to reduce swelling and pain.
- Engaging in physical therapy to improve:
- Flexibility and range of motion.
- Strength in the surrounding muscles, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings.
- Using braces or patellar straps for added support.
Advanced Treatments
For severe or persistent cases, advanced therapies may be recommended:
- Corticosteroid injections to manage inflammation.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy to promote healing.
- Shockwave therapy to stimulate tissue repair.
Surgical Options
In rare cases where conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary. This involves repairing the damaged portion of the tendon.
Consulting a patellar tendinitis surgery doctor in Cheshire is essential for understanding surgical options and expected outcomes.
Patellar tendonitis prevention
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing patellar tendinitis:
- Gradual progression in physical activity to avoid overuse.
- Incorporating strength and flexibility exercises into training routines.
- Wearing proper footwear to support the knees and legs.
- Ensuring proper warm-up and cool-down routines during workouts.
By adopting these strategies, individuals can maintain knee health and minimize the risk of injury.
Living with Patellar Tendinopathy
Managing patellar tendinopathy involves:
- Adapting sports and daily activities to avoid aggravating the condition.
- Following a structured rehabilitation plan.
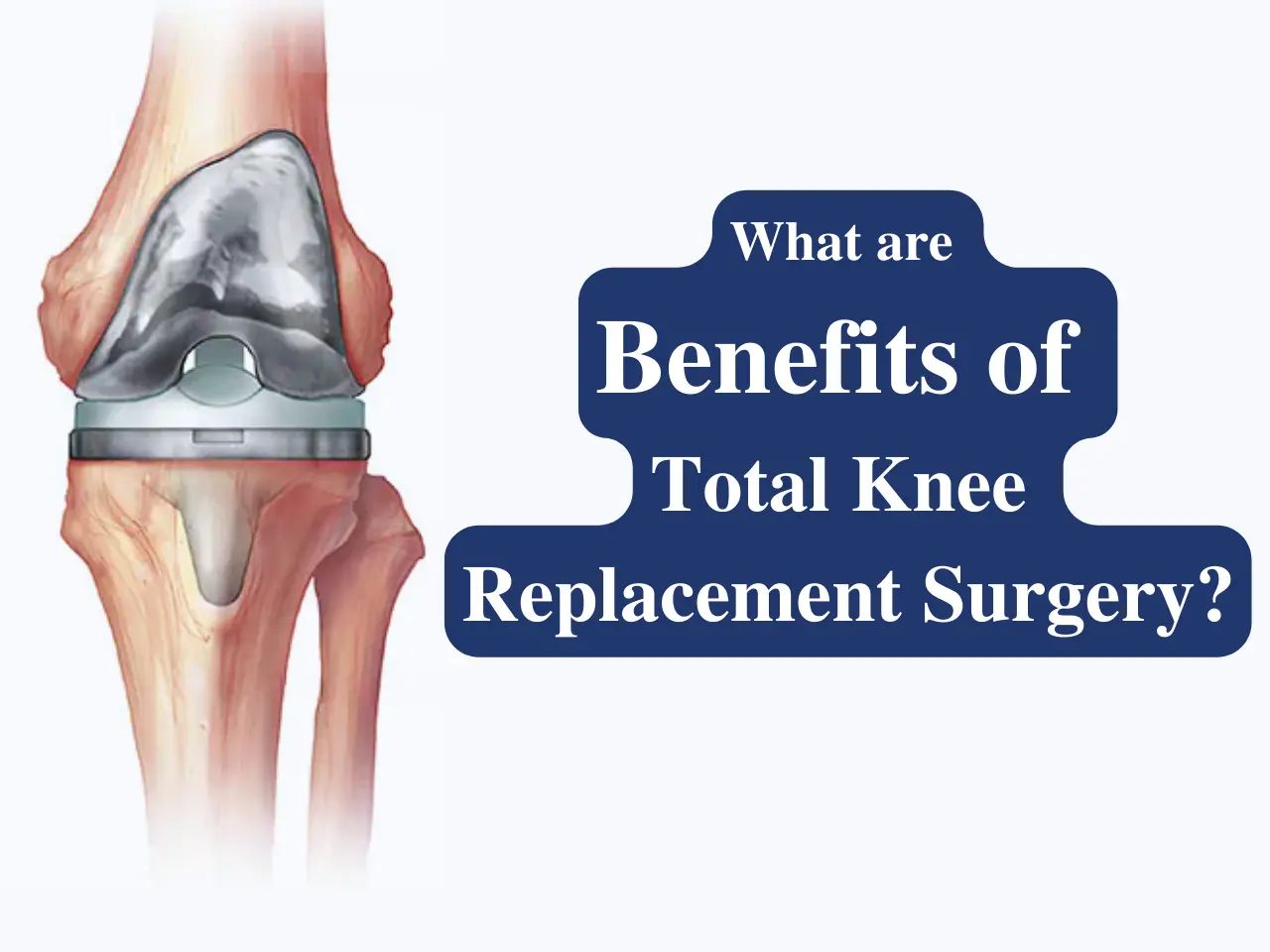
- Seeking advanced treatments or even knee replacement in Cheshire if the condition progresses to severe stages.
Conclusion
Patellar tendinopathy is a common yet manageable condition.
Understanding what patellar tendinitis is, its symptoms, causes, and treatments can empower individuals to take proactive steps toward recovery.
Seeking expert care from specialists like Mr. Nikhil Pradhan can ensure optimal outcomes and a return to an active lifestyle.
Prioritizing prevention and early intervention are key to maintaining healthy knees for years to come.