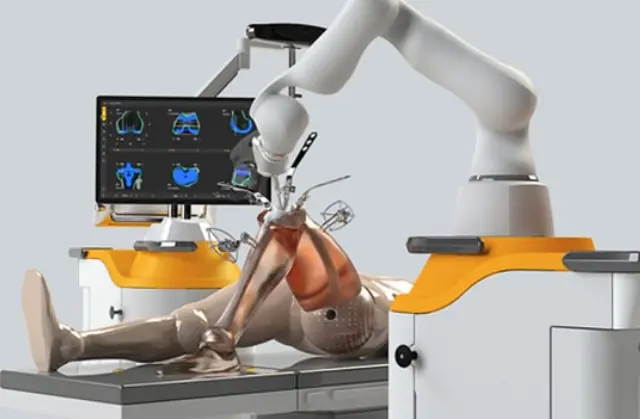
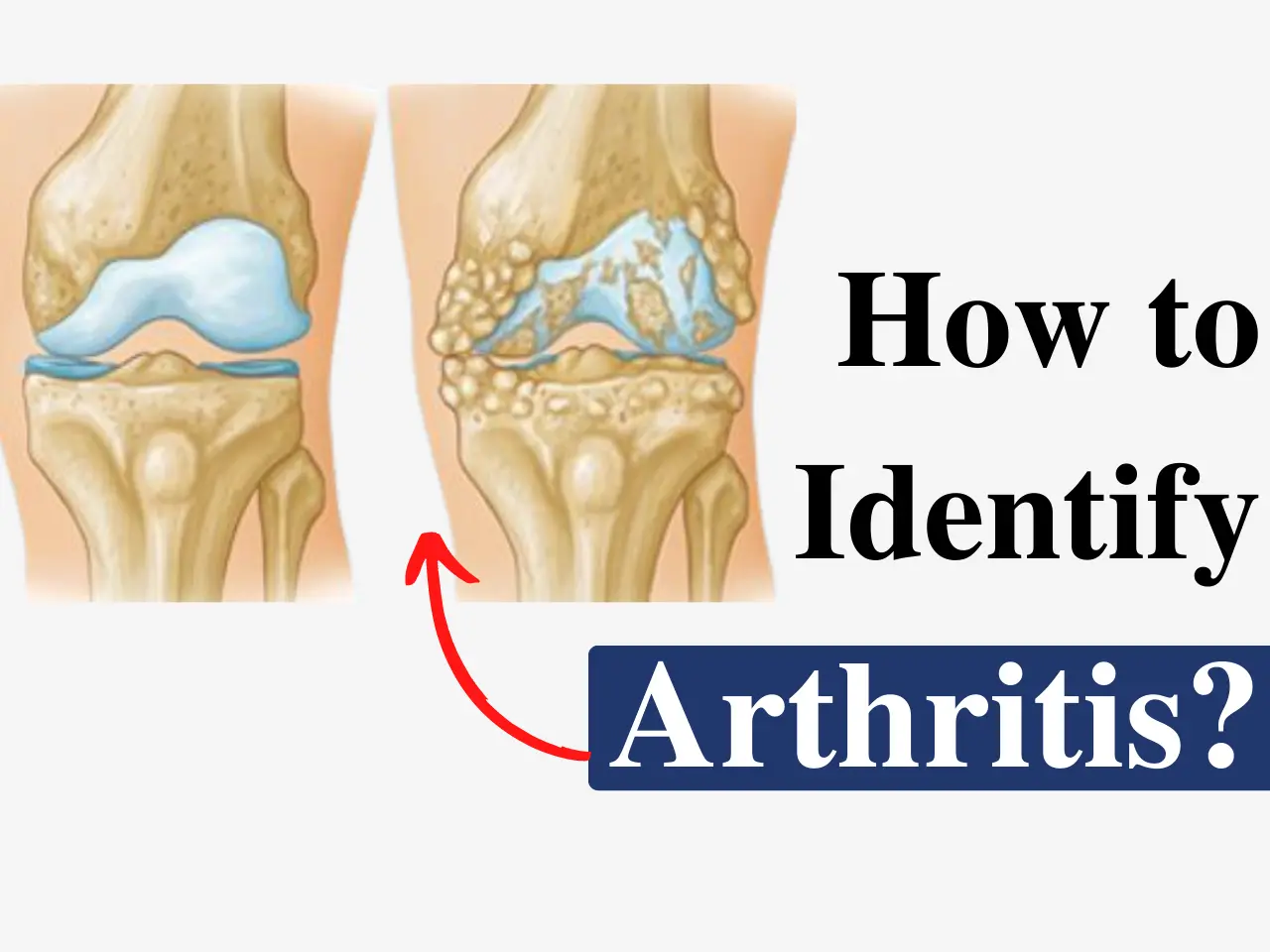
Knee ligament injuries are common and can significantly impact joint stability and mobility. Ligaments are tough bands of tissue connecting bones within the joint, crucial for providing stability and controlling the range of motion. When these ligaments are injured, it can lead to pain, swelling, and instability in the knee.
Knee Ligament Injuries: Understanding the Basics
The knee is a complex joint where bones meet, and ligaments provide crucial stability. These ligaments are tough, fibrous bands of tissue that connect the bones of your knee, namely the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone), and fibula (calf bone).
The four major knee ligaments include:
Types of Knee Ligaments
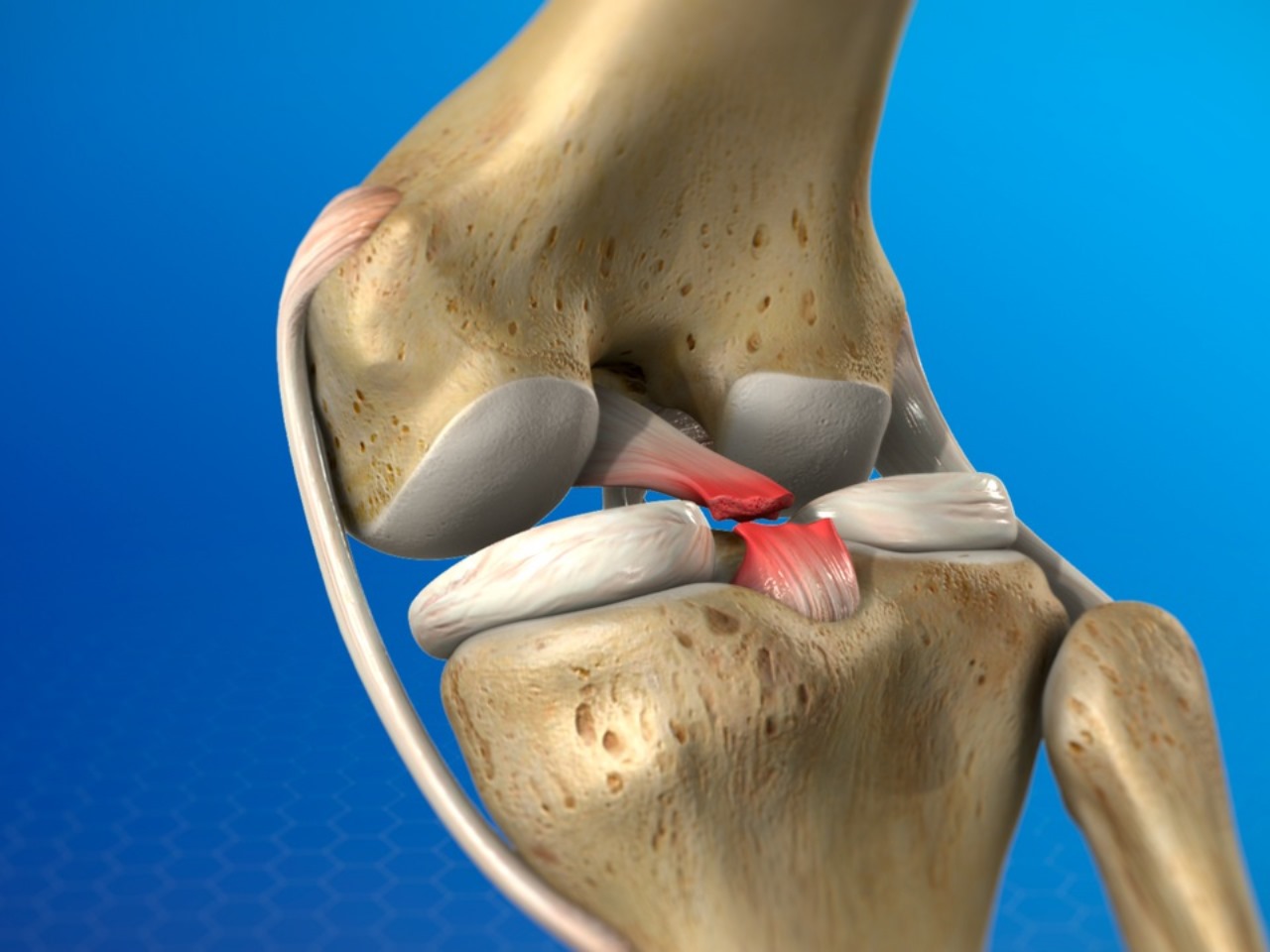
- ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament): Located in the center of the knee, it helps prevent the shin bone from sliding out in front of the thigh bone.
- PCL (Posterior Cruciate Ligament): Situated at the back of the knee, it prevents the shin bone from moving backward too far.
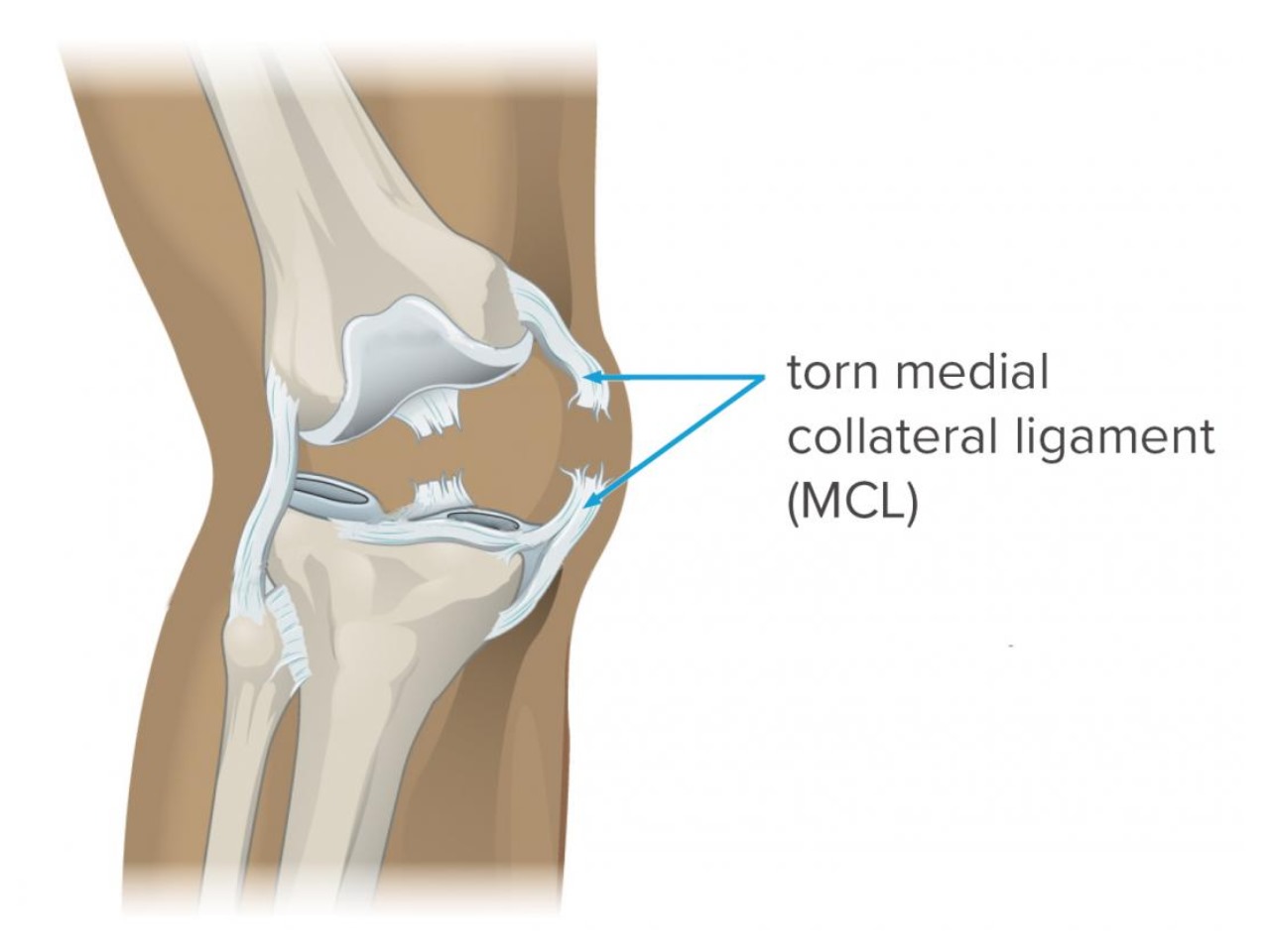
- MCL (Medial Collateral Ligament): Runs along the inner side of the knee, providing stability to the inner knee.
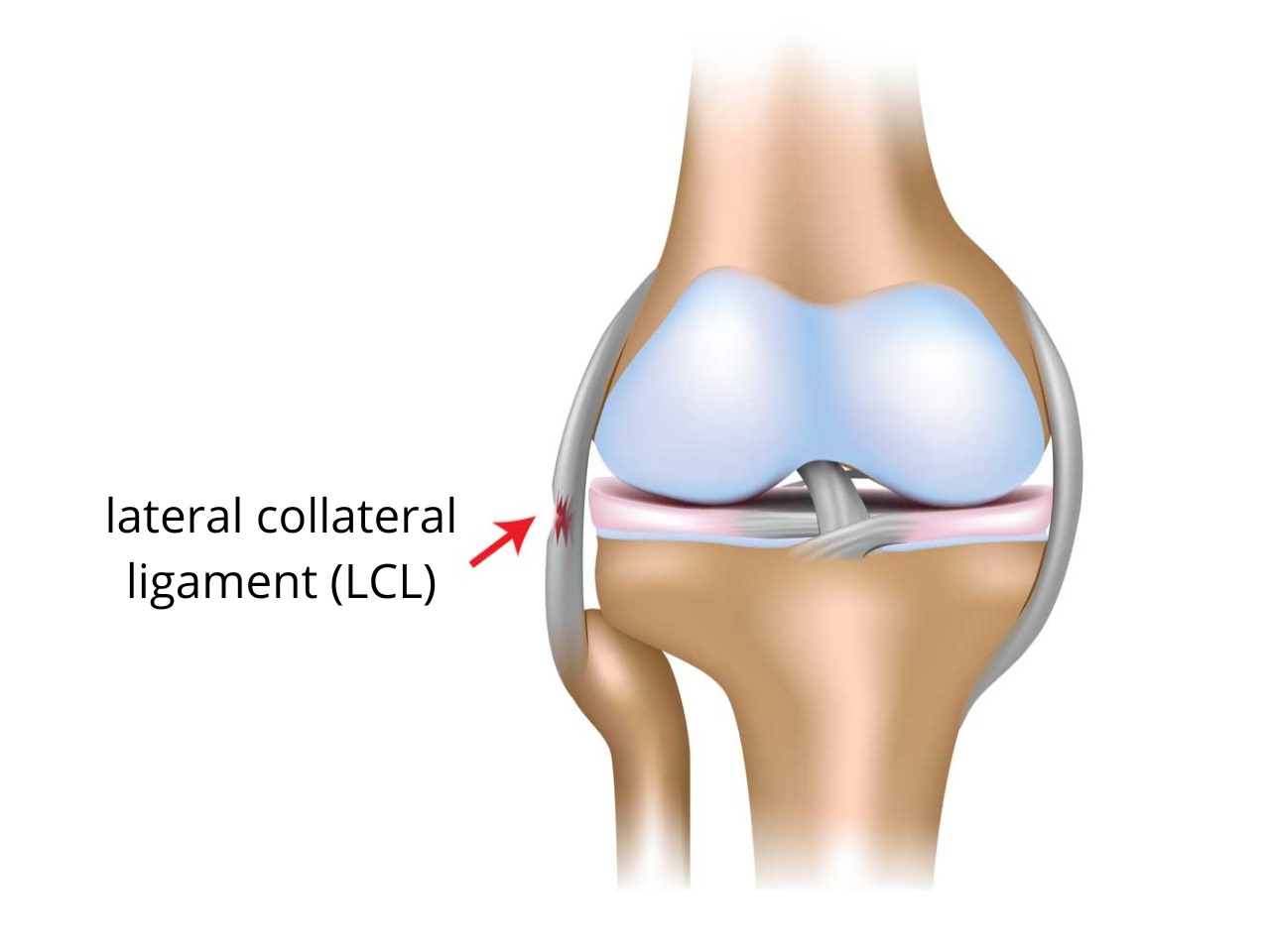
- LCL (Lateral Collateral Ligament): Runs along the outer side of the knee, stabilizing the outer knee.
Causes of Knee Ligament Injuries
Ligament tears can happen due to various reasons, including:
- Sudden twists or pivots: This is a common cause in sports like football, basketball, and skiing.
- Direct blows to the knee: Falls or car accidents can cause ligament tears.
- Overuse: Repetitive movements, particularly in sports, can lead to gradual weakening and tears.
- Landing awkwardly: Jumping or landing incorrectly can put excessive stress on the ligaments.
The impact of a ligament tear can vary depending on the severity. A minor sprain might cause pain and stiffness, while a complete tear can lead to significant instability and difficulty walking.
Impact of Knee Cruciate Ligament Injuries
Functional Implications
Knee ligament injuries can lead to:
- Instability in the knee joint: Feeling of the knee giving way during movement.
- Difficulty in daily activities and sports: Reduced ability to participate in physical activities.
Long-Term Effects-
- Risk of osteoarthritis: Chronic instability and joint wear may accelerate joint degeneration.
- Impact on joint health: Proper treatment and rehabilitation are crucial to prevent long-term complications.
Symptoms of Knee Ligament Injuries
Common Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the severity but often include:
- Pain and tenderness around the knee: Especially during movement or when touching the affected area.
- Swelling and stiffness: Inflammation around the injured ligament.
- Instability or feeling of giving way: Difficulty in bearing weight or performing activities requiring knee stability.
Specific Symptoms by Ligament Type
- ACL: Often accompanied by a popping sound at the time of injury and significant swelling.
- MCL: Pain and tenderness on the inner side of the knee, particularly when bending or twisting the knee.
Diagnosis of Knee Ligament Injuries
Physical Examination
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Assessment of knee stability: Checking for signs of instability or abnormal joint movement.
- Range of motion tests: Evaluating the knee’s flexibility and mobility.
Imaging Tests
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of soft tissues, helping to assess ligament damage.
- X-rays: Used to rule out fractures or other bone-related injuries.
Treatment Options for Knee Ligament Injuries
Non-Surgical Treatments
Initial treatment often includes:
- Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE): To reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Strengthening exercises to improve knee stability and flexibility.
Surgical Treatments
- ACL Reconstruction Surgery: Involves replacing the torn ACL with a graft from another tendon, restoring knee stability.
- Repair or reconstruction: Depending on the severity, other ligaments may also require surgical repair or reconstruction.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
Recovery involves:
- Structured physical therapy: Gradual progression of exercises to regain strength and range of motion.
- Return to sports: Guided by healthcare professionals to ensure safe and effective rehabilitation.
Prevention of Knee Ligament Injuries
Injury Prevention Strategies
Reducing the risk of knee ligament injuries includes:
- Proper warm-up and stretching routines: Before engaging in physical activities.
- Using protective gear: Such as knee braces or supports during sports activities.
Conclusion
Knee ligament injuries can significantly impact daily life and sports participation. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for timely intervention and effective recovery.
If you experience symptoms of a knee ligament injury, seeking prompt medical attention and following a comprehensive rehabilitation plan can enhance outcomes and minimize long-term complications.