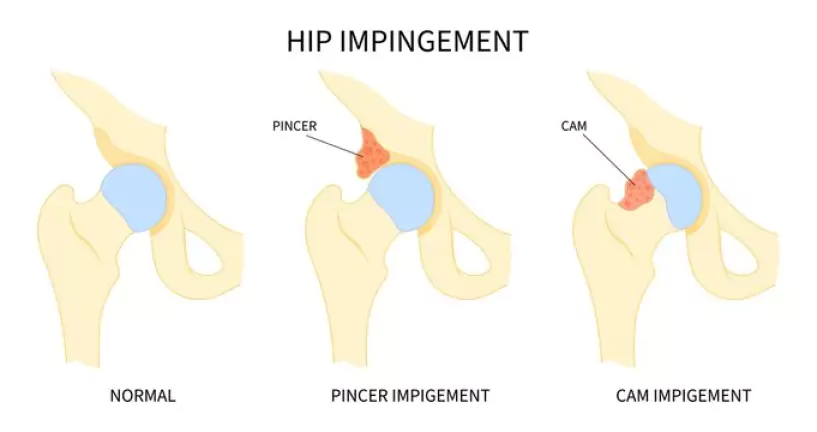
Hip impingement, also known as Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI), is a common condition that affects the hip joint, causing pain and restricted movement.
This condition occurs when the ball-and-socket joint of the hip does not move smoothly, leading to friction that damages the joint over time.
If left untreated, hip impingement can progress to osteoarthritis and other severe hip problems.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage the symptoms effectively.
Prof. Nikhil Pradhan, a Senior Orthopaedic Consultant in the Northwest of the UK, specializes in hip, joint, and knee surgeries with over 30 years of experience in treating hip impingement and other orthopaedic conditions.
What is Hip (Femoroacetabular) Impingement?
Hip impingement, or Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI), is a condition where excess bone growth or abnormal bone shapes in the hip joint cause friction during movement.
This friction leads to pain, stiffness, and damage to the cartilage and labrum, affecting overall hip function.
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint where the femoral head (ball) fits into the acetabulum (socket).
When these bones do not fit perfectly, it results in hip impingement, leading to discomfort and potential long-term damage.
Hip Impingement Symptoms
- Gradual onset of hip pain, especially during movement or physical activities.
- Stiffness and restricted range of motion in the hip joint.
- Pain that worsens with prolonged sitting, walking, or sports activities.
- Clicking, locking, or catching sensation in the hip.
- Discomfort while climbing stairs, bending, or performing high-impact movements.
Hip Impingement Causes
Several factors contribute to hip impingement, including:
- Structural abnormalities: Excess bone growth (bone spurs) in the femoral head or acetabulum.
- Repetitive motion injuries: Common among athletes involved in sports like football, hockey and ballet.
- Genetic factors: Some individuals may be predisposed to hip abnormalities.
- Previous hip injuries: Trauma, fractures, or childhood hip conditions leading to impingement.
- Underlying conditions: Hip dysplasia, osteoarthritis, or labral tears.
Types of Hip Impingement
- Cam Impingement
- Caused by an irregularly shaped femoral head that cannot move smoothly within the socket.
- More common in young, active individuals.
- Pincer Impingement
- Occurs when the acetabulum (hip socket) covers too much of the femoral head.
- Leads to excessive friction and restricted movement.
- Combined Impingement
- A combination of both Cam and Pincer impingement, causing significant hip dysfunction.
Hip Impingement Risk Factors
- Age and activity level: More common in young athletes and physically active individuals.
- Sports participation: Football, hockey, martial arts, and ballet increase the likelihood of hip impingement.
- Genetic predisposition: Family history of hip abnormalities.
- Previous hip conditions: Childhood hip disorders, such as hip dysplasia.
- Gender differences: Males are more prone to Cam impingement, while females often develop Pincer impingement.
Hip Impingement Treatments in Cheshire
- Non-Surgical Treatments
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding high-impact activities that worsen hip pain.
- Physical therapy: Strengthening exercises to improve hip stability and flexibility.
- Pain management: Use of anti-inflammatory medications and corticosteroid injections.
- Weight management: Reducing stress on the hip joint.
- Surgical Treatments
Hip Arthroscopy (Minimally Invasive Surgery)
- A procedure to reshape the femoral head and acetabulum to reduce friction.
- Removal of excess bone growth and damaged cartilage.
- Faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Hip Replacement Surgery
- Recommended for severe hip impingement cases that lead to arthritis.
- Replacing the damaged hip joint with a prosthetic implant.
- Available at Hip Replacement Clinics in Cheshire under expert care.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Post-surgery rehabilitation exercises to strengthen the hip and restore mobility.
- Guided physiotherapy sessions for a gradual return to daily activities.
- Expected recovery timeline: Varies depending on treatment type and individual health.
Preventing Hip Impingement
- Regular stretching and strengthening exercises to maintain joint flexibility.
- Proper posture and movement techniques to reduce strain on the hips.
- Avoiding overuse injuries by balancing physical activity and rest.
Conclusion
Hip impingement can be a debilitating condition if left untreated, but with the right diagnosis and treatment, individuals can regain mobility and lead pain-free lives.
Early intervention is key to preventing long-term damage.
For expert consultation and Hip Impingement Treatments in Cheshire, Prof. Nikhil Pradhan offers specialized care tailored to individual needs.
If you’re experiencing persistent hip pain, seek professional advice to explore the best treatment options.