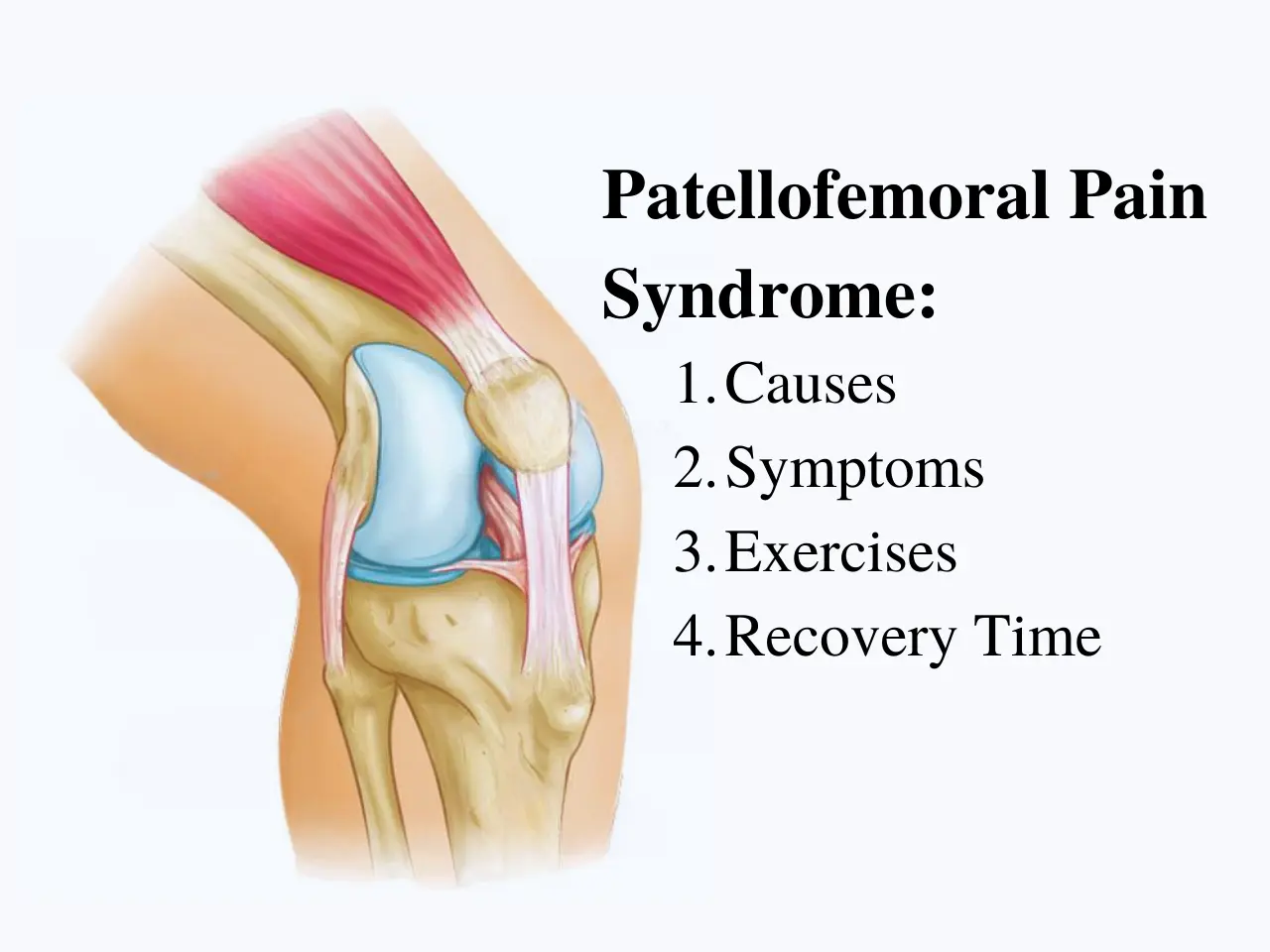
Cartilage plays a crucial role in joint function, providing cushioning and enabling smooth movement. However, when damaged, it can lead to significant pain, stiffness, and mobility issues.
Mr. Nikhil Pradhan, a leading knee replacement surgeon in Cheshire, has over 30 years of experience in treating knee cartilage injuries and other orthopedic conditions.
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent long-term joint deterioration.
Understanding Cartilage and Its Role in Joint Health
What is Cartilage?

Cartilage is a flexible yet strong connective tissue found in various parts of the body, including joints, ribcage, and the ears.
It serves several vital functions:
- Acts as a shock absorber, reducing friction between bones.
- Provides structural support without rigidity.
- Helps in smooth joint movement.
There are three types of cartilage:
- Hyaline Cartilage – Found in joints, nose, and ribcage.
- Elastic Cartilage – Present in the ear and larynx.
- Fibrocartilage – Found in intervertebral discs and knee meniscus.
What are Knee Cartilage Injuries?
Cartilage injuries, particularly in the knee, can lead to pain, stiffness, and impaired movement. These injuries are common in athletes and aging individuals.
Types of Knee Cartilage Injuries
- Chondromalacia Patella – Softening and breakdown of cartilage under the kneecap.
- Meniscus Tears – Damage to the fibrocartilage that cushions the knee.
- Osteochondritis Dissecans – A condition where cartilage and underlying bone separate.
- Traumatic Cartilage Injuries – Caused by direct impact, sports, or accidents.
Symptoms of Cartilage Damage in Knee
- Persistent knee pain, especially during movement.
- Swelling and stiffness in the affected joint.
- Clicking or grinding sensations in the knee.
- Limited range of motion and difficulty walking.
- Knee instability or locking sensation.
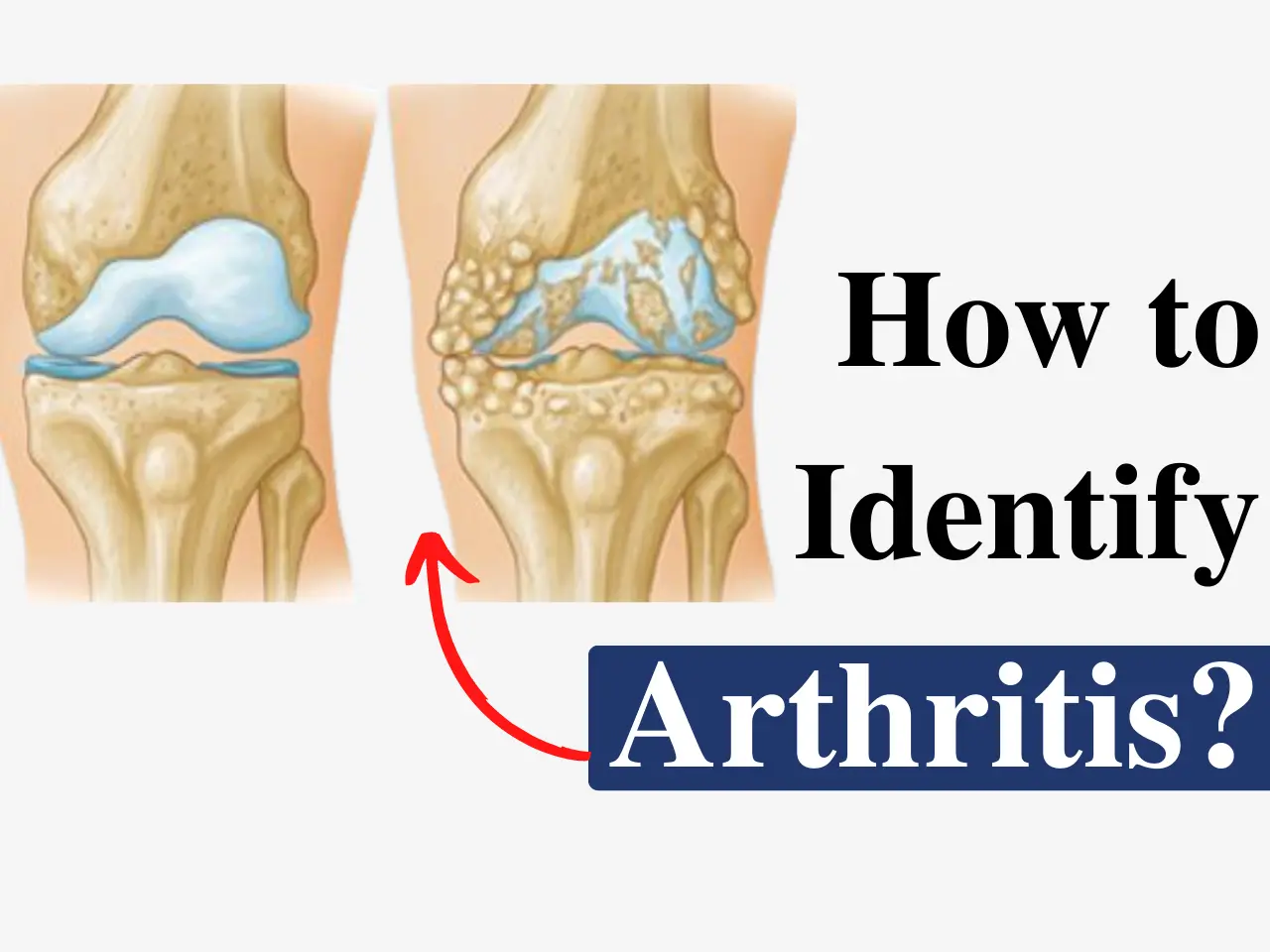
Cartilage Damage Causes & Risk Factors
Cartilage Damage Causes
- Acute Trauma – Sports injuries, falls, or car accidents.
- Repetitive Stress – Excessive joint usage in athletes and labor-intensive jobs.
- Aging – Natural wear and tear leading to degeneration.
- Obesity – Increased weight places stress on knee cartilage.
- Medical Conditions – Conditions like osteoarthritis contribute to cartilage deterioration.
Risk Factors of Knee Cartilage Injuries
- High-impact activities (football, basketball, skiing).
- Weak muscles and lack of joint flexibility.
- Previous knee injuries or surgeries.
- Genetic predisposition to joint problems.
Diagnosing Cartilage Damage
Clinical Examination
- Detailed medical history and assessment of symptoms.
- Physical examination to evaluate joint movement and swelling.
Imaging Tests
- X-rays – Used to check for bone fractures or arthritis.
- MRI scans – Provide a detailed view of cartilage and soft tissues.
- Arthroscopy – A minimally invasive procedure to directly visualize cartilage damage.
Cartilage Damage Treatment
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Rest and Activity Modification – Avoiding activities that aggravate the injury.
- Physical Therapy – Strengthening muscles around the knee to reduce strain.
- Medications – Anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers.
- Viscosupplementation Injections – Best injection for knee arthritis, helping improve lubrication and reduce pain.
Exercises for Cartilage Damage
- Low-impact exercises – Swimming, cycling, and walking.
- Strengthening exercises – Leg raises, squats, and hamstring stretches.
- Flexibility exercises – Improve range of motion and reduce stiffness.
Surgical Treatments
- Arthroscopic Debridement – Removing loose cartilage fragments.
- Microfracture Surgery – Stimulating new cartilage growth.
- Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS) – Transplanting healthy cartilage.
- Knee Cartilage Transplantation – Using donor cartilage for large defects.
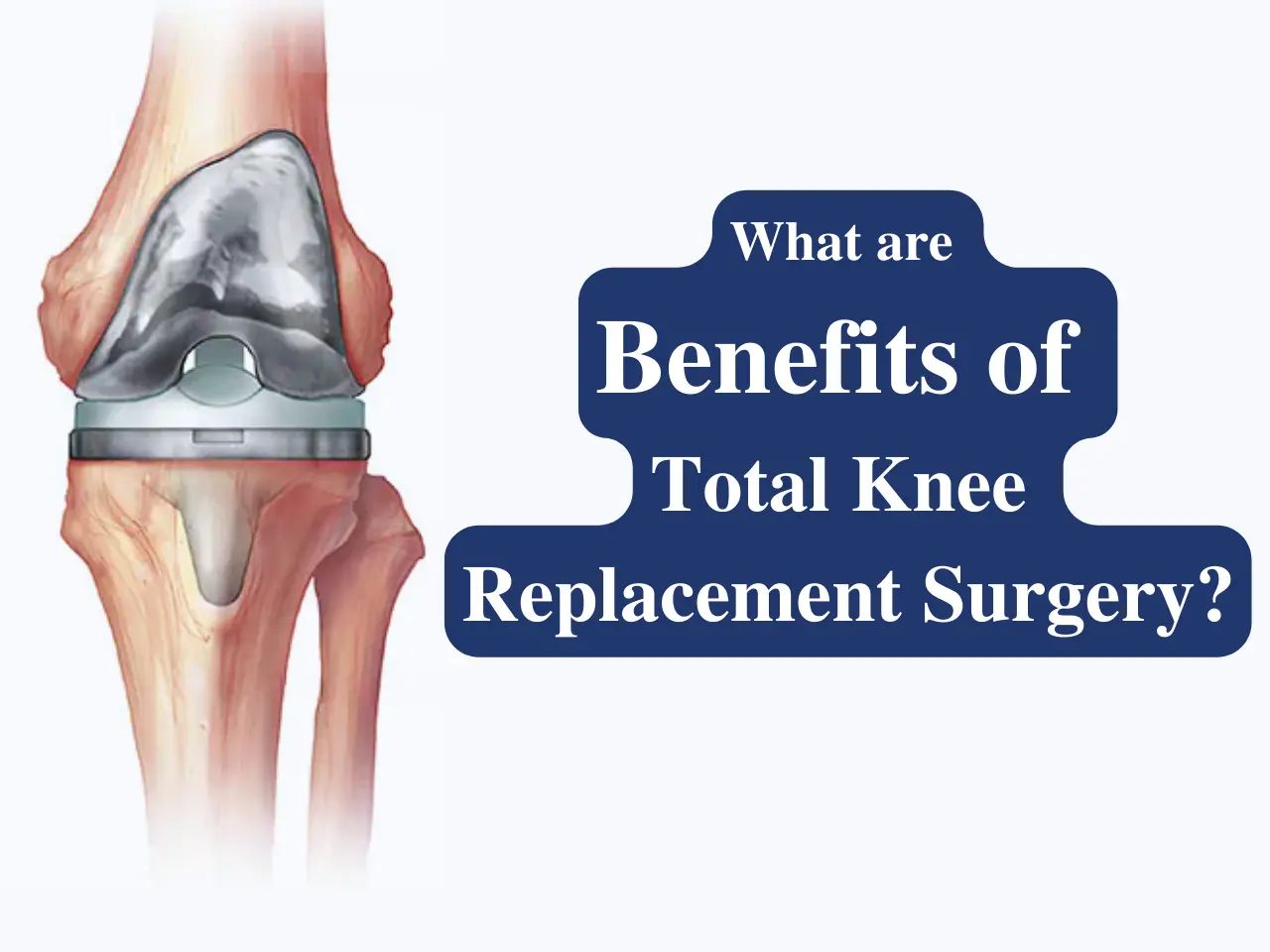
- Knee Replacement Surgery – Performed by a knee arthritis surgeon in Cheshire for severe cases.
Knee Cartilage Injury Recovery Time & Rehabilitation
- Recovery depends on the severity of the injury and treatment method.
- Minor injuries: 4-6 weeks with physiotherapy.
- Surgical recovery: 3-6 months, including post-operative rehab.
- Gradual return to daily activities under medical supervision.
Knee Cartilage Damage Treatment in Cheshire – Consult Mr. Nikhil Pradhan
Mr. Nikhil Pradhan offers expert treatment for knee cartilage injuries in Cheshire, using advanced surgical and non-surgical methods. With a patient-centric approach, he ensures optimal recovery for each individual.
FAQs
- What is the main cause of cartilage damage?
Cartilage damage is often caused by trauma, repetitive stress, aging, obesity, or underlying medical conditions like arthritis.
- What are the common symptoms of cartilage damage in the knee?
Symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, limited mobility, clicking or grinding sensations, and knee instability.
- Can cartilage damage heal on its own?
Minor cartilage injuries can improve with rest and therapy, but severe damage may require medical intervention, including surgery.
- What is the best injection for knee arthritis?
Viscosupplementation injections, such as hyaluronic acid, help lubricate the joint and reduce pain.
- What is the knee cartilage injury recovery time?
Recovery time varies depending on severity. Minor injuries heal within 4-6 weeks, while surgical recovery can take 3-6 months.
- What are the best exercises for cartilage damage?
Low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and stretching exercises help strengthen muscles and improve mobility.
- Where can I get the best knee cartilage damage treatment in Cheshire?
Consult Mr. Nikhil Pradhan, a top knee replacement surgeon in Cheshire, for expert treatment and personalized care.
Conclusion
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing cartilage damage effectively.
If you’re experiencing knee cartilage injuries, seek expert care from Mr. Nikhil Pradhan, a highly experienced knee arthritis surgeon in Cheshire.
Book an appointment today for the best treatment options available.