As we age, or if we’re recovering from orthopaedic procedures like hip or knee replacement, maintaining strong bones and healthy joints becomes more important than ever.
While physical therapy and exercise are key, your diet plays a critical role in long-term joint function and bone density.
In this blog, Mr. Nikhil Pradhan, an experienced orthopaedic surgeon in Cheshire, shares expert insights on the best foods for bone health and the best vitamins for joints, helping you make smart dietary choices that support your mobility, recovery, and overall health.
Why Nutrition Matters for Bone and Joint Health?
Our bones and joints require a steady supply of nutrients to stay resilient, lubricated, and pain-free.
Poor nutrition can lead to:
- Weakened bones (osteopenia or osteoporosis)
- Joint stiffness and inflammation
- Slower recovery after orthopaedic surgery
For patients undergoing hip or knee replacement, following a diet rich in bone strengthening foods and vitamins for bone and joint health can accelerate healing and improve surgical outcomes.

Best Foods for Bone Health
- Calcium-Rich Foods for Bones
Calcium is the cornerstone of bone health. It helps build and maintain bone structure and prevents loss of bone density.
Top calcium-rich foods include:
- Dairy: milk, cheese, and yogurt
- Leafy greens: kale, bok choy, spinach
- Fortified almond or soy milk
- Tofu and edamame
- Almonds and sesame seeds
Including these calcium rich foods for bones in your daily diet can significantly reduce the risk of fractures and support recovery after surgery.
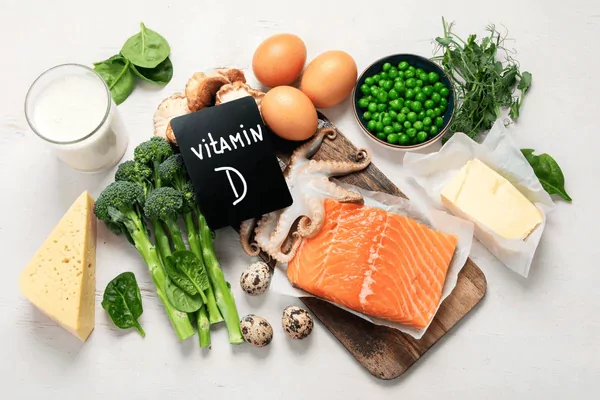

- Vitamin D for Bone Health
Calcium cannot be absorbed efficiently without vitamin D, making it a crucial part of any bone-strengthening plan.
Best sources of Vitamin D:
- Fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel
- Egg yolks
- Fortified dairy and cereals
- Safe sun exposure (15–20 minutes daily)
Vitamin D for bone health is especially important for those who live in colder climates or have limited sun exposure.
- Magnesium for Bones and Joints
Magnesium supports calcium absorption and bone mineral density. It also plays a role in joint and muscle function.
Magnesium-rich foods include:
- Nuts and seeds (especially pumpkin and almonds)
- Whole grains like brown rice and oats
- Bananas and avocados
- Dark chocolate (in moderation)
Magnesium for bones and joints is often overlooked but is just as vital for skeletal health.
Best Vitamins for Joints and Cartilage
- Vitamin C
Vitamin C supports the production of collagen, a key component of cartilage, tendons, and ligaments.
Rich sources include:
- Oranges and citrus fruits
- Strawberries
- Broccoli and bell peppers
- Kiwi and guava
- Vitamin K
Vitamin K is involved in calcium regulation and bone mineralization, reducing the risk of bone fractures.
Sources of Vitamin K:
- Leafy greens like spinach and kale
- Brussels sprouts
- Fermented foods like natto
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s are powerful anti-inflammatory foods for joint pain. They help reduce swelling and stiffness, especially for those with arthritis or post-surgical inflammation.
Top omega-3 foods:
- Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and herring
- Flaxseeds and chia seeds
- Walnuts
Bone Strengthening Foods: Daily Essentials
Create meals that include a mix of essential nutrients for bones and joints.
Sample bone-friendly plate:
- Grilled salmon (Omega-3 + Vitamin D)
- Quinoa and kale salad (Calcium + Magnesium)
- Greek yogurt with strawberries (Calcium + Vitamin C)
These bone strengthening foods can be incorporated into every meal to support lifelong joint health.
Joint Health Supplements: When Diet Isn’t Enough
In some cases—especially for elderly patients or those with dietary restrictions—joint health supplements can help bridge nutritional gaps.
Popular supplements include:
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin: supports cartilage
- Collagen peptides: promotes joint elasticity
- Turmeric/Curcumin: natural anti-inflammatory
- Calcium + Vitamin D3: ideal for bone density
Always consult a qualified orthopaedic surgeon in Cheshire like Mr. Nikhil Pradhan before starting any supplement routine, especially if you are preparing for or recovering from surgery.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods for Joint Pain
Chronic joint pain and arthritis are often triggered or worsened by inflammation. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods for joint pain can bring natural relief.
Top anti-inflammatory choices:
- Turmeric and ginger
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries)
- Olive oil and nuts
- Leafy greens
- Green tea
Avoid processed foods, refined sugar, and excessive alcohol, which can worsen inflammation and joint stiffness.
Diet Tips for Joint Replacement Patients
Patients recovering from hip or knee replacement surgery must pay extra attention to their diet.
Helpful dietary guidelines include:
- Prioritize protein for tissue repair
- Eat calcium and vitamin D-rich foods to support bone healing
- Stay hydrated to reduce inflammation
- Avoid excessive sodium and sugar
- Eat small, frequent meals to maintain energy
Mr. Nikhil Pradhan, a trusted joint replacement surgeon in Cheshire, recommends working with a dietitian for personalised meal plans after surgery.
When to See a Specialist?
If you experience:
- Persistent joint stiffness or pain
- Decreased mobility
- Frequent bone fractures or weakness
It’s time to consult a specialist. Mr. Nikhil Pradhan is a highly experienced orthopaedic surgeon in Cheshire offering comprehensive care and surgical solutions, including joint replacement for long-term relief.
Conclusion
A healthy diet is one of the most powerful tools in protecting your bones and joints.
With the right combination of bone strengthening foods, calcium rich foods for bones, and vitamins for bone and joint health, you can stay mobile, flexible, and pain-free as you age.
If you’re experiencing joint issues or planning for surgery, consult Mr. Nikhil Pradhan, a leading joint replacement surgeon in Cheshire, for tailored guidance and expert care.